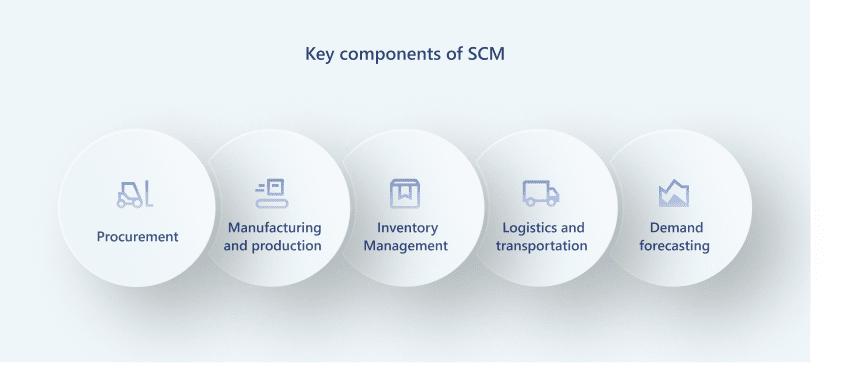
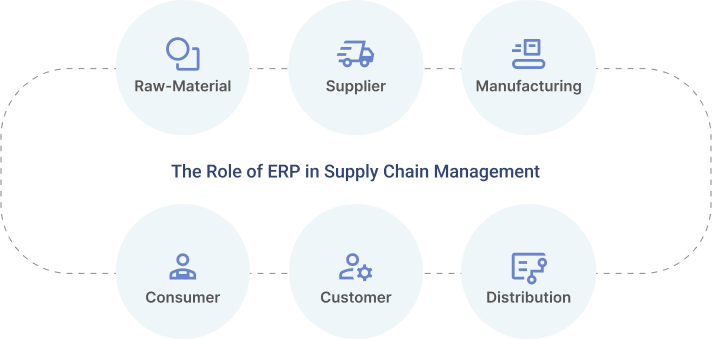
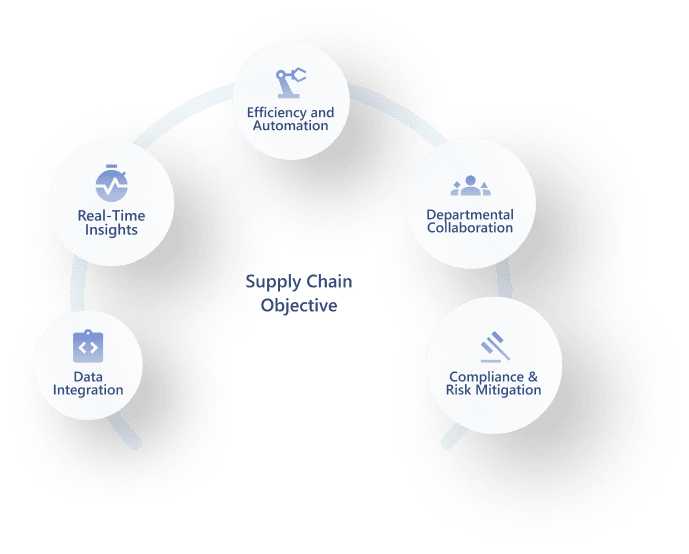
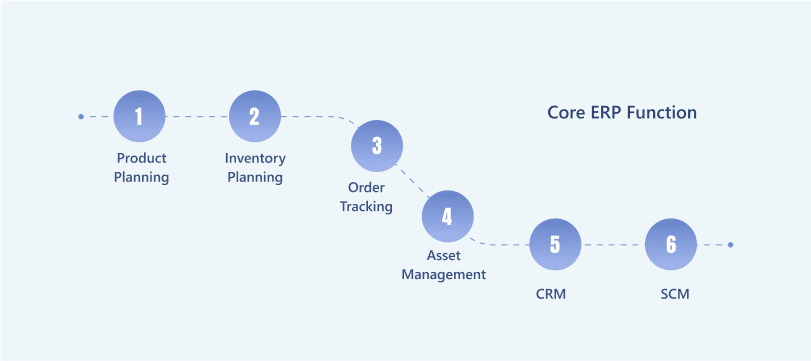
Chapter 4: What Are the Benefits of ERP in Supply Chain Management?
This chapter will show the key benefits you can experience after implementing an ERP system for your supply chain process.
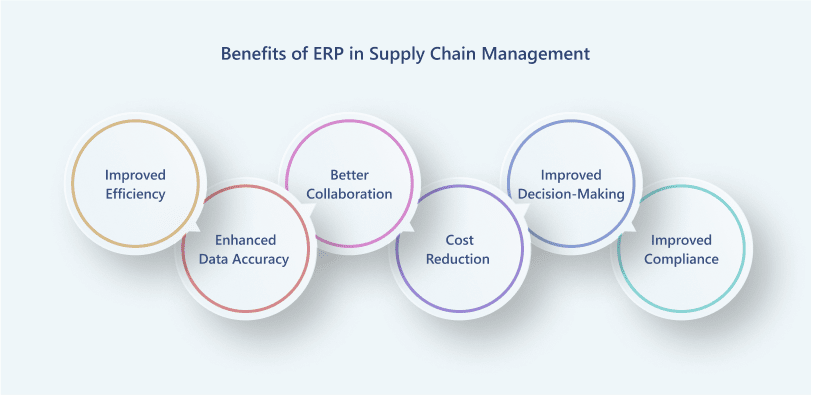
4.1 Improved Efficiency
The key to effective supply chain management is efficiency. ERP systems increase productivity by standardizing procedures throughout the supply chain and automating repetitive work.
Streamlined Procedures Throughout Supply Chain Functions:
ERP and supply chain systems combine manufacturing, logistics, inventory, and procurement procedures into a single platform. This integration guarantees smooth workflows and lessens delays brought on by divided operations.
For example, you have access to real-time inventory level updates. Procurement procedures can be set up to automatically start when inventory levels hit reordering points to guarantee ideal inventories.
Automation of Routine Operations:
ERP systems eliminate human error and save time by automating repetitive operations, including order processing, invoicing, and inventory updates. This helps employees to focus on strategic tasks, increasing overall productivity.
4.2 Enhanced Data Accuracy
Data is essential for supply chain decision-making to be effective, accurate, and trustworthy. ERP systems reduce errors and give users instant access to reliable data.
Real-Time Updates and Visibility:
ERP in supply chain management enables organizations to track inventories, orders, and shipments in real time, enabling them to spot problems early and take preventative action. ERP systems, for example, can assist a shop in tracking inventory levels and making real-time adjustments to replenishment plans to satisfy seasonal demand.
Minimizing Manual Data Entry Errors:
ERP systems let you guarantee data integrity across departments by automating data entry and integrating procedures, which removes errors brought on by human error. This can enable you to guarantee reduced wait times, more accurate reporting, and higher levels of client satisfaction.
4.3 Better Collaboration and Communication
ERP systems foster collaboration by centralizing data and guaranteeing transparency amongst departments and supply chain partners.
Cross-Departmental Cooperation:
Teams from sales, manufacturing, finance, and logistics may access shared data, guaranteeing coordination and preventing misunderstandings.
For example, the sales staff forecasts higher demand and modifies the ERP systems accordingly. Real-time data access and schedule adjustments are possible for the production team, and real-time budget allocation is possible for the finance department.
Collaboration between Suppliers and Customers:
ERP systems allow suppliers and customers to communicate efficiently through portals, exchanging shipment information, order updates, and performance reviews. As a result, the supply chain becomes more resilient, and connections with suppliers and consumers are strengthened.
4.4 Cost Reduction
ERP systems' capacity to lower costs throughout the supply chain is one of their most significant benefits.
Better Inventory Management:
ERP systems give firms information about inventory turnover, which helps them keep the right amount of goods on hand and steer clear of overstocking or understocking. You can save on carrying expenses and enhance cash flow management.
Improved Demand Forecasting:
By reducing waste and preventing needless production, predictive analytics technologies in Enterprise Resource Planning ERP and Supply Chain Management SCM systems assist companies in making more accurate demand forecasts. There are fewer spoils, overproductions, and stockouts, which lowers costs.
4.5 Improved Decision-Making
ERP systems enable companies to make data-driven, well-informed decisions that increase productivity and profitability.
Real-Time Data Access:
To make prompt and precise decisions, decision-makers can access the most recent data on client orders, supplier performance, and inventory levels.
For example, a logistics manager can reroute goods using real-time traffic and weather data to guarantee on-time delivery.
Analytics for Prediction:
Advanced analytics technologies assist organizations in anticipating shifts in the market and making appropriate plans by offering insights into emerging patterns. For example, a factory can utilize predictive analytics to expect shortages of raw materials and find alternate suppliers beforehand.
4.6 Improved Compliance and Risk Management
ERP systems assist businesses in maintaining adherence to industry norms and laws, lowering their financial and legal risks.
Compliance Tracking:
Monitoring compliance metrics throughout the supply chain guarantees your operation follows trade laws, environmental standards, and product safety are followed.
Risk management:
ERP systems help firms take corrective action before problems worsen by detecting possible risks in real-time.